Level 4
Level 4
Measuring Storm Effects
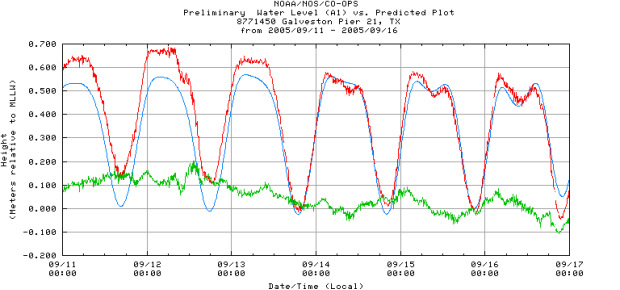
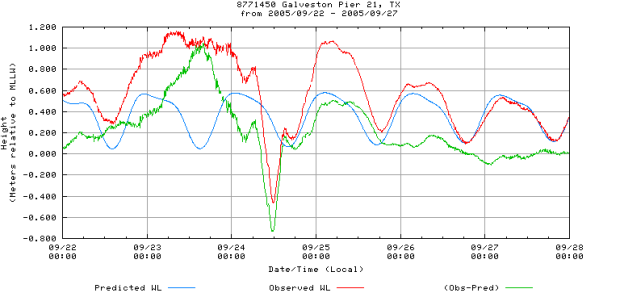
Storms can have a big impact on local water levels in coastal areas. A storm surge happens when water is pushed toward the shore by high powered winds from a storm such as a hurricane. The storm interacts with the normal tide to create a storm tide that can increase the normal water height by 4 to 5 meters (15 feet) or more. These events can cause extreme flooding in coastal areas. Most coastlines in the United States are only 3 meters (10 feet) or less above mean sea level, which means that storms can be very dangerous for people who live near the coast.
Use the tide chart below to compare tide heights before and during a storm an check your understanding. Then try making your charts to look at the effects of storms using real data.